OER4Schools/Introduction to enquiry based learning: Difference between revisions
| Line 268: | Line 268: | ||
= Guiding questions to help you plan an enquiry-task = | = Guiding questions to help you plan an enquiry-task = | ||
{| style="border-spacing:0;" | {| style="border-spacing:0;" | ||
| Line 277: | Line 275: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="border:0.035cm solid #000000;padding:0.176cm;"| Questions have many answers. | | style="border:0.035cm solid #000000;padding:0.176cm;"| Questions have many answers. | ||
''Examples: '' | ''Examples: '' | ||
''What could be the consequences of water contamination? How does a balanced diet help us? How could we use flowers of plants? Suggest ways to prevent spread of malaria in your community?'' | ''What could be the consequences of water contamination? How does a balanced diet help us? How could we use flowers of plants? Suggest ways to prevent spread of malaria in your community?'' | ||
| style="border:0.035cm solid #000000;padding:0.176cm;"| Questions elicit relations between ideas and extended ideas. | | style="border:0.035cm solid #000000;padding:0.176cm;"| Questions elicit relations between ideas and extended ideas. | ||
''Examples:'' | ''Examples:'' | ||
''What would happen if only inorganic fertilizers are used for growing plants? What connections do you see between climate of a region and its vegetation? Why is the water in the nearby pond not safe for drinking?'' | ''What would happen if only inorganic fertilizers are used for growing plants? What connections do you see between climate of a region and its vegetation? Why is the water in the nearby pond not safe for drinking?'' | ||
|} | |} | ||
These questions will according to Dr Benjamin Bloom be ‘higher-level’ thinking questions. The levels (“taxonomy”) of questions that Bloom has developed form a framework used by many teachers across the world to develop questions that help students progress from concrete to abstract thinking. You may remember it was introduced in the VVOB handout “Questioning the questions” as part of the homework for Session 4.1. The taxonomy classifies learning into six progressive levels of complexity and abstraction: | These questions will according to Dr Benjamin Bloom be ‘higher-level’ thinking questions. The levels (“taxonomy”) of questions that Bloom has developed form a framework used by many teachers across the world to develop questions that help students progress from concrete to abstract thinking. You may remember it was introduced in the VVOB handout “Questioning the questions” as part of the homework for Session 4.1. The taxonomy classifies learning into six progressive levels of complexity and abstraction: | ||
# Knowledge – students should: describe; identify; recall. | # Knowledge – students should: describe; identify; recall. | ||
| Line 303: | Line 297: | ||
On this scale, knowledge is the lowest-order thinking skill and creation is the highest. Enquiry-based learning aims to help students learn to analyse, evaluate and create. As your planning progresses, consider how you think your enquiry project might be extended to do this? | On this scale, knowledge is the lowest-order thinking skill and creation is the highest. Enquiry-based learning aims to help students learn to analyse, evaluate and create. As your planning progresses, consider how you think your enquiry project might be extended to do this? | ||
# Can you make use of the OpenOffice spreadsheet to create a database on the possible resources that you require for such an event? | # Can you make use of the OpenOffice spreadsheet to create a database on the possible resources that you require for such an event? | ||
# Consider also what are some administrative requirements you need to attend to to organise such an event (e.g. Do you need permission from an authority/parents? Do you need to invite a specialist speaker to talk about the topic?) | # Consider also what are some administrative requirements you need to attend to to organise such an event (e.g. Do you need permission from an authority/parents? Do you need to invite a specialist speaker to talk about the topic?) | ||
'''Part 2: '''Complete the ICT tutorials. Consider and be ready to share in the next session how the OpenOffice spreadsheet and/or GeoGebra can be a useful tool for enquiry-based lessons? | '''Part 2:''' Complete the ICT tutorials. Consider and be ready to share in the next session how the OpenOffice spreadsheet and/or GeoGebra can be a useful tool for enquiry-based lessons? | ||
= Acknowledgements = | = Acknowledgements = | ||
We thank YouthLearn Initiative at Education Development Center (http://www.youthlearn.org/learning/planning/lesson-planning/how-inquiry/how-inquiry inquiry) and Futurelab (http://www.enquiringminds.org.uk/terms_of_use/) for kindly allowing us to use the material from their website. We also thank Professor Katja Maaß for permission to use the Primas video on the impact of inquiry based learning on students and teachers. | We thank YouthLearn Initiative at Education Development Center (http://www.youthlearn.org/learning/planning/lesson-planning/how-inquiry/how-inquiry inquiry) and Futurelab (http://www.enquiringminds.org.uk/terms_of_use/) for kindly allowing us to use the material from their website. We also thank Professor Katja Maaß for permission to use the Primas video on the impact of inquiry based learning on students and teachers. | ||
Revision as of 22:06, 3 September 2012
"You can't teach people everything they need to know. The best you can do is position them where they can find what they need to know when they need to know it."
Seymour Papert, MIT
Review of homework
![]() Whole Group Discussion (11 min).
Whole Group Discussion (11 min).
- Did you find that the use of the assessment inventory helped you to reflect on how you have made use of AfL in your classroom? How?
- What techniques did you try out to maintain an effective pace in your lesson? Did you find that your lesson was still over or under-running? Why was that?
- How did your students respond to the sequencing activity on the computers (if you have tried it out)? Were there any difficulties in using it? How would you prepare better the next time?
- Were there any challenges in preparing your portfolio?
Objectives for this session
In the next four sessions, we will explore a way of teaching and learning that encourages students to take the initiative to pose questions and explore their curiosity about the world around them, through a process of enquiry.
The objectives for this session are to
- learn about the aims and process of enquiry-based learning
- help participants to start preparing for enquiry-based learning through a series of lessons, a ‘project day’ or ‘field trip’ for their mathematics or science classes.
Resources needed for this session:
- large white piece of paper
- different colours of markers or coloured pens
- computer/laptop/netbook and internet.
By now the facilitator should appreciate the importance of pacing each session well by making good use of time-management techniques. This unit, like many of the others, will involve participants in many discussion, hands-on and planning activities. You may need to intervene and move things on if participants are spending too much time on an activity (in relation to the time you have available). Or you may decide that they can benefit from continuing an activity longer than anticipated, if you judge that most/all participants are still gaining new knowledge/experience from that activity. Please take note of our recommendations about whether each activity is crucial or optional. This should help you to decide on whether to spend more or less time on it.
A Taste of Enquiry-Based Learning
![]() Whole Group (11 min). In this activity called “PMI” - “Positives, Minuses, Interesting” there are no correct answers.The PMI involves considering the positive, negative and interesting points related to a specific scenario. It was originally developed by Edward de Bono, father of the “thinking skills” movement. It encourages learners to look at both sides of a situation and also to be creative when considering the interesting possibilities.
Whole Group (11 min). In this activity called “PMI” - “Positives, Minuses, Interesting” there are no correct answers.The PMI involves considering the positive, negative and interesting points related to a specific scenario. It was originally developed by Edward de Bono, father of the “thinking skills” movement. It encourages learners to look at both sides of a situation and also to be creative when considering the interesting possibilities.
Consider the following scenario: Plants can now walk in our world!
(It is important to realise that plants do not need to move because they make their own food by photosynthesis – animals have to move in order to forage for food)
What would be some positives, minuses or interesting points you can think of, if this scenario was actually true?
Possible responses:
- P (positives): the plant could move to where there is more light or water
- M (minusses): the plant would waste energy by moving
- I (interesting): We have to be sensitive and aware of plants walking on the roads and in our houses.
For further examples, navigate to:
![]() Whole group discussion (11 min). You may have heard of “enquiry-based learning” (EBL) being practised in other subjects (e.g. geography) or in higher grades through farming or industry projects. For instance, you may have heard of teachers bringing their students outside the classroom to learn about commercial and subsistence farming. The quotes below shows you what two Zambian teachers have thought about enquiry-based learning; read the text, then offer your own understanding of EBL as a group.
Whole group discussion (11 min). You may have heard of “enquiry-based learning” (EBL) being practised in other subjects (e.g. geography) or in higher grades through farming or industry projects. For instance, you may have heard of teachers bringing their students outside the classroom to learn about commercial and subsistence farming. The quotes below shows you what two Zambian teachers have thought about enquiry-based learning; read the text, then offer your own understanding of EBL as a group.
Abel: To me, Enquiry-based learning is a flexible, student-centred method of teaching and learning. It engages learners with a complex problem or scenario that is open-ended to allow a variety of responses or solutions. Its success depends on the guidelines teachers give about how students can be involved in self-directed enquiry. This way of teaching caters to different abilities of students and encourages them to learn on their own, even beyond schooling. This is what life-long learning should be. It may also help students to develop leadership skills as they manage complex projects with their friends.
Agness: Enquiry-based learning reminds me of projects focusing on industry or farming, where a teacher can take the learners out of the classroom to experience and analyse the actual farming process, what vegetables are grown within the area or how cotton is processed into a fabric and then designed into a dress. Such a form of learning is stimulating for the students and encourages them to be actively involved in asking questions and seeking out new ideas or evidence.
What is Enquiry-Based Learning?
![]() Watch video and Whole Group discussion (11 min). Watch the following three clips showing three different teachers trying to introduce some form of enquiry in the classroom. Think about these questions as you are watching and discuss at the end of watching the three clips:
Watch video and Whole Group discussion (11 min). Watch the following three clips showing three different teachers trying to introduce some form of enquiry in the classroom. Think about these questions as you are watching and discuss at the end of watching the three clips:
- Did the three different teachers introduce the lesson in a way that is similar or different from a usual maths or science lesson in your classroom? How?
- Do you think that such a way of ‘setting up’ the lesson can engage the students productively over time? Why? Do you think your own students will enjoy this kind of lesson?
- What questions did the teachers pose to arouse the curiosity and interest of the students?
- What kinds of classroom organisation or resource are needed to support this way of teaching?
Try to focus on these specific questions above rather than on the teaching style of the teacher (e.g. the classroom management/mannerism)!
Clip 1: Noxolo 3D Shape - 1.2.10 - “Now we come to an activity...”
Noxolo is setting up the activity for students to identify which net diagram goes with which and finding the properties of each (faces/vertices/edges)
Clip 2: Exponential Clips - 2.1-1, 2.3-18, 2.4-23 and 2.4-21 - “The Power of 2”: What would you choose?
- 2.1-1: Whole clip (Pindi introducing the problem)
- 2.3-18: Whole clip (Pindi telling class they are going to school hall) [can we edit 2.3-18 so that teachers can just see bits of Pindi saying that she is bringing students to the hall]
- 2.4-23: Whole clip (Group work activity at drawing the graph)
- 2.4-21: 0:00 to 0:17 (Pindi asking the groups to gather)
These clips show Pindi introducing a problem involving exponentials and telling students they will be going to the school hall to draw the graph. Why do you think they went to the school hall?
Clip 3: How can we learn mathematics through using used plastic bottles for building a house?
http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=17pW9ahYTck
Facilitator may like to highlight that there is a spectrum of practices of enquiry-based learning: from one that is very teacher-directed (teacher chooses the questions and organises the activities) to one that is more student-directed (teachers provides only a stimulus picture and students decide what more they would like to find out. If there is time, ask participants to discuss what would be the most appropriate form of enquiry-based learning for their classrooms currently. Most likely it will be the former rather than the latter - which is fine to start with!
![]() Whole group discussion (11 min). Continue the whole group discussion, augmenting the definition of enquiry-based learning to make it your own.
Whole group discussion (11 min). Continue the whole group discussion, augmenting the definition of enquiry-based learning to make it your own.
Benefits of Enquiry-Based Learning
![]() Individual reading task (11 min). Read the following summary texts on the benefits of enquiry-based learning and think about whether you are convinced by the claims of the authors? Make notes or annotations on the page if you have a paper copy and want to do so.
Individual reading task (11 min). Read the following summary texts on the benefits of enquiry-based learning and think about whether you are convinced by the claims of the authors? Make notes or annotations on the page if you have a paper copy and want to do so.
Enquiry-based learning helps students to be:
- inquisitive and curious about things that they experience in their everyday lives
- able to pose problems, ask questions, and recognise issues that they would like to explore
- able to develop an understanding that knowledge changes over time as people challenge, shape and contribute to it
- responsible for deciding what they learn and how they learn it
- confident that they too can challenge, shape and contribute to knowledge
- aware that there are always multiple perspectives for looking at, analysing and understanding things
- able to propose solutions to problems and questions, and to know how to pursue these solutions.
Enquiry-based teaching supports teachers to be:
- open to students’ ideas about the processes and directions of their learning
- keen to learn about how ideas and knowledge are produced in subjects other than their own
- able to research topics and make connections between ideas
- interested in students’ lives and cultures
- able to challenge students to critique, expand and build upon the knowledge they have from their own experiences and ideas.
(Taken from: http://www.enquiringminds.org.uk/)
Impact on learning
Enquiry-based teaching and learning have been shown to increase motivation and interest of learners and teachers, and can significantly increase achievement on standardised tests. The increased focus required of the learners to discuss and be involved in practical work means that there will be less emphasis on writing down factual information only. On the whole, students will be involved in more higher order thinking and this increases the level of challenge of learning for all the learners.
(Taken from “Bright Ideas in Primary Science” evaluation in 16 schools: http://www.brookes.ac.uk/schools/education/rescon/azsttp.html
![]() Whole Group Discussion (11 min). The benefits of enquiry have been outlined but what are the issues or concerns that might arise? How can these be addressed?
Whole Group Discussion (11 min). The benefits of enquiry have been outlined but what are the issues or concerns that might arise? How can these be addressed?
The facilitator should make use of the opportunity to discuss with the participants what are some challenges in making use of enquiry-based learning. It may be the case that some participants would choose to focus on the negatives - lack of suitable venues, managing students, lack of time, unwilling to plan for lessons that will span across days. It will be helpful to discuss their concerns while at the same time to direct their attentions to the possibilities and strengths of enquiry-based learning
Planning an outdoor activity
![]() Small Group Work (11 min). Each group of 3-4 participants should have access to the following material:
Small Group Work (11 min). Each group of 3-4 participants should have access to the following material:
- large white piece of paper
- different colours of markers or coloured pens
Imagine that you are very interested to bring your students outside the classroom to learn certain maths or science concepts using an authentic ‘real-life’ approach. Up to now, the ideas are just ‘lingering’ in your mind. You are curious to know of the possibilities and what other participants think about it! Let’s call this learning experience a “field trip” or “project day”.
Nominate a leader in your group who will read out the instructions and facilitate the group work by writing down the ideas on the sheet of white paper.
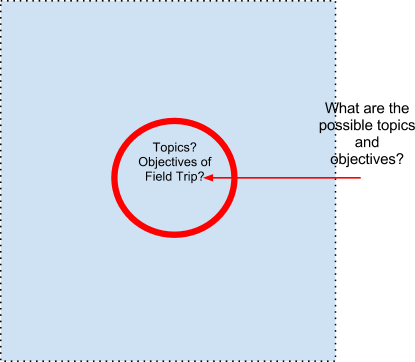
Identify Possible Objectives
Take a coloured marker/pen and write "Objectives of Field Trip" in the center of the paper. Now circle it, as shown in the illustration below. Brainstorm on one or two maths and science topics that you would like to focus on and write within the circle. Write down as well what are the possible lesson objectives of the field trip – to help all of you to focus on generating more ideas later.
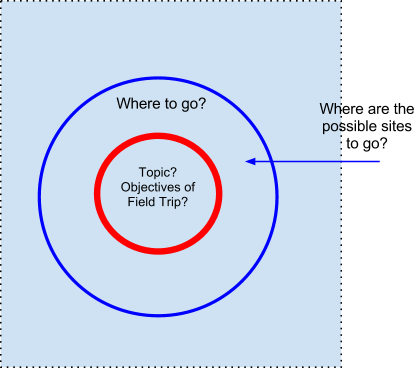
Identify Possible Sites of Learning
Use a different colour marker/pen and draw a bigger circle around the previous circle. Write down “Where to go?” at the top of the circle. Brainstorm and write down within the bigger circle, where are the possible sites you could bring your students to learn about the maths/science concepts outside the classroom. You may need to consider the practical issues of whether the site is safe for the students and whether it is easy to bring a class of students to that particular venue. (You can choose the school grounds if you want or it may in fact take place just within your classroom!) Also, consider whether the sites will be able to help students learn the objectives of your lessons.
Advancing Ideas of Possible Activities
Draw a rectangle around the previous shapes (outside the outer circle) using a different coloured marker/pen. As shown in the illustration, brainstorm and write down within the rectangle, what can we do at the various sites? Again, consider the safety and convenience issues, and whether the activities can actually serve to help students achieve the learning objectives (or whether the classroom will be actually be much better!)
Mapping and Presentation of Possible Ideas
Try to follow the different paths of ideas by connecting the ideas in different logical ways:
On our field trip which I intend to help the students to learn ___________ (topic and objective of field trip?), we could bring the students to ___________ (where to go?) where we can ______________ (do what?).
In your group try to come up with as many different ideas as possible and decide on what are the ideas that you feel would be most workable/not so workable. State your reasons for saying so. Identify some resources that you will need to prepare for the field trip.
Present your outcomes to the rest of the participants. It will be helpful to be as specific as possible so for instance, “a lesson on a science topic on plants in the school field outside the classroom for students to explore the plants there” will be much too vague!
The facilitator should highlight to the participants that they themselves have gone through a structured enquiry-based activity in a group setting, to help them find out about the possible ways to organise a field trip for their students.
Compare the activities that were developed. Are those actually enquiry-based activities or do they have the potential to become them? Are the questions sufficiently open-ended and rich? Which of the other features of enquiry that we have identified do they have? If none, why? If so, ask them to consider why they think this is an enquiry-based learning activity?
How possible would it be for their students to make use of enquiry-based learning? Do they think that such a method of learning will be well-received by the students and their parents?
Making use of ICT in Enquiry-Based Learning
You may want to limit the time spent on these tasks spent within the workshop. You could interrupt, say after 20 minutes, to discuss the homework. However, if there is time after the workshops, participants could always return to these activities. It is essential to allow time to introduce the homework before the session ends.
To use ICT in an investigative way requires that both teachers and learners are sufficiently familiar with the technology and software, or the teacher spends the whole time troubleshooting problems of using the technology and software instead of addressing the more important enquiry skills and learning objectives Developing this familiarity through progressively more complex use of ICT needs careful thought. For a starter, addressing the whole class to demonstrate features/procedures of using ICT can be most efficient rather than speaking to groups in turn.
In this session, we suggest that you familiarise yourself with the use of the spreadsheet function in OpenOffice and/or with GeoGebra. It is likely that you may need to complete the activity as homework.
![]() Individual Task (11 min). Activity 1. This activity will orientate you to make use of OpenOffice for creating spreadsheets and databases which can be useful for investigating maths and science problems. You will need to access a computer/laptop/netbook and internet. Access a web browser and navigate to this page: http://inpics.net/calc.html
Individual Task (11 min). Activity 1. This activity will orientate you to make use of OpenOffice for creating spreadsheets and databases which can be useful for investigating maths and science problems. You will need to access a computer/laptop/netbook and internet. Access a web browser and navigate to this page: http://inpics.net/calc.html
We suggest that you go through some of the exercises on the page in this order:
This activity will orientate you to make use of OpenOffice for creating spreadsheets and databases which can be useful for investigating maths and science problems. You will need to access a computer/laptop/netbook and internet. Access a web browser and navigate to this page: http://inpics.net/calc.html
We suggest that you go through some of the exercises on the page in this order:
1. Basic Calculations
2. Formatting Worksheets
3. Manipulating Data
- Move, copy, and paste
- Add / delete columns
- Add / delete rows
- Employ multiple worksheets
- Employ AutoFill
- Insert / delete worksheets
4. Advanced Calculations
5. Making Data Visible
![]() Individual Task (11 min). Activity 2. This activity will orientate you to make use of GeoGebra to create basic polygons. You will need to access a computer/laptop/netbook and internet. Access a web-browser and navigate to this page: http://mathandmultimedia.com/geogebra/
Individual Task (11 min). Activity 2. This activity will orientate you to make use of GeoGebra to create basic polygons. You will need to access a computer/laptop/netbook and internet. Access a web-browser and navigate to this page: http://mathandmultimedia.com/geogebra/
This activity will orientate you to make use of GeoGebra to create basic polygons.
You will need to access a computer/laptop/netbook and internet. Access
a web-browser and navigate to this page:
http://mathandmultimedia.com/geogebra/
We will suggest that you go through the exercises in the page in this order:
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 1 – Constructing an Equilateral Triangle
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 2 – Constructing an Isosceles Triangle
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 3 – Constructing a Right Triangle
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 4 – Constructing a Square
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 5 – Constructing a Rectangle
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 6 - Constructing a Parallelogram
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 7 – Constructing a Rhombus
- GeoGebra Basic Construction 9 – Constructing a Kite
(In the Zambian context, these may be suitable for Grade 5 upwards.)
Homework
PORTFOLIO. Continue collecting evidence for your OER4Schools portfolio by keeping track of your planning and implementation of an enquiry project, and reflecting on what you are learning as you go through the unit. Collect paper/electronic documents to show the whole process, beginning in this workshop session and throughout Unit 5. Please include copies (e.g. photographs/photocopies) of student work throughout the stages they go through (not just finished outcomes). Remember to include challenges you faced as well as benefits.
As we are nearing the end of the year’s programme, we would also like to return to the 'most significant change' technique and ask you to use your portfolio to create a story illustrating the biggest change you feel you have made in your thinking and practice over the year.
Part 1: Start planning for an enquiry-based ‘project day’ or ‘field trip’ for your own classroom and share your ideas in the next session. The questions (similar to the small group activity just now) below should be a useful starting point for your planning. Remember that the project or field trip should allow the students to explore an enquiry idea in some depth (and not just answer some closed and surface questions).
- What is a suitable topic for the grade(s) of your students?
- What are suitable lesson objectives/success criteria?
- Where would be a suitable venue for the event?
- What kind of overall enquiry question or task could you pose? Can you phrase some further sample questions that ask learners what they know/think about some aspects of your chosen topic? What might they then like to know/find out? (Remember what ‘open-ended’ and ‘deep’ questions are (see Session 2.1 and table below).
Guiding questions to help you plan an enquiry-task
| ‘Open-ended’ Questions | ‘Deep’ Questions |
| Questions have many answers.
Examples: What could be the consequences of water contamination? How does a balanced diet help us? How could we use flowers of plants? Suggest ways to prevent spread of malaria in your community? |
Questions elicit relations between ideas and extended ideas.
Examples: What would happen if only inorganic fertilizers are used for growing plants? What connections do you see between climate of a region and its vegetation? Why is the water in the nearby pond not safe for drinking? |
These questions will according to Dr Benjamin Bloom be ‘higher-level’ thinking questions. The levels (“taxonomy”) of questions that Bloom has developed form a framework used by many teachers across the world to develop questions that help students progress from concrete to abstract thinking. You may remember it was introduced in the VVOB handout “Questioning the questions” as part of the homework for Session 4.1. The taxonomy classifies learning into six progressive levels of complexity and abstraction:
- Knowledge – students should: describe; identify; recall.
- Comprehension – students should: translate; review; report; restate.
- Application – students should: interpret; predict; show how; solve; try in a new context.
- Analysis – students should: explain; infer; analyse; question; test; criticise.
- Evaluation – students should: assess; compare and contrast; appraise; argue; select.
- Creation – students should: design; create; arrange; organise; construct.
On this scale, knowledge is the lowest-order thinking skill and creation is the highest. Enquiry-based learning aims to help students learn to analyse, evaluate and create. As your planning progresses, consider how you think your enquiry project might be extended to do this?
- Can you make use of the OpenOffice spreadsheet to create a database on the possible resources that you require for such an event?
- Consider also what are some administrative requirements you need to attend to to organise such an event (e.g. Do you need permission from an authority/parents? Do you need to invite a specialist speaker to talk about the topic?)
Part 2: Complete the ICT tutorials. Consider and be ready to share in the next session how the OpenOffice spreadsheet and/or GeoGebra can be a useful tool for enquiry-based lessons?
Acknowledgements
We thank YouthLearn Initiative at Education Development Center (http://www.youthlearn.org/learning/planning/lesson-planning/how-inquiry/how-inquiry inquiry) and Futurelab (http://www.enquiringminds.org.uk/terms_of_use/) for kindly allowing us to use the material from their website. We also thank Professor Katja Maaß for permission to use the Primas video on the impact of inquiry based learning on students and teachers.