Factors Affecting Lesson Design: Difference between revisions
m (Fixing tagging, as well as cross-curric, vocabulary, distance learning, share practice, DfE, DfEScience templates) |
No edit summary |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<noinclude>{{ORBITreading}}</noinclude> | |||
=Factors affecting lesson design and the design process= | =Factors affecting lesson design and the design process= | ||
Latest revision as of 18:17, 6 February 2015
- Aspects Of Engagement
- Assessment Overview
- Assessment for Learning Introduction
- Assessment for Learning Research Summary
- Building Capacity in School
- Classroom Management - Thinking Point
- Creating Engagement
- Developing Higher Order Scientific Enquiry Skills
- Developing Your Teaching
- Factors Affecting Lesson Design
- Fibonacci Project
- Group Talk - Benefits for Science Teaching
- Group Work - Practical Considerations
- Group Work - Research Summary
- Improving Reading - Research Summary
- Improving Writing - Research Summary
- Inclusive Teaching in Mathematics
- Inclusive Teaching in Science
- Modelling Introduction
- Purposes and characteristics of whole-class dialogue
- Questioning Research Summary
- Speaking and Listening in Group Work
- TESSA Working With Teachers
- Teaching Learning Developing Approaches to CPD
- Teaching Learning and Whole School Improvement
- The Importance of Speaking and Listening
- The Process of Lesson Design
- The educational value of dialogic talk in whole-class dialogue
- The impact of enquiry-based science teaching on students' attitudes and achievement
- Types Of Question
- Using Digital Video in Professional Development
- Whole Class Work - Research Summary
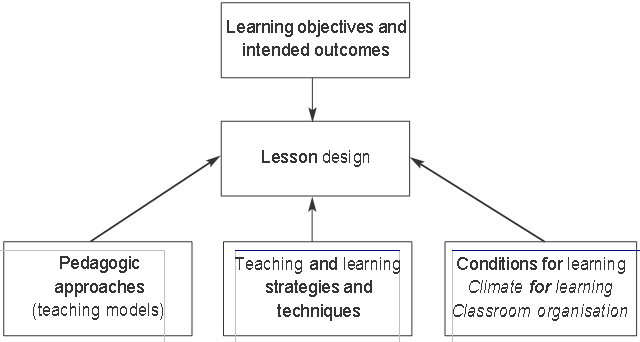
Factors affecting lesson design and the design process
Effective, experienced teachers consider the full range of factors when designing lessons.
The learning objective(s) for a lesson will come from the scheme of work. Having clearly defined the learning objective, it is important to go one step further and consider the intended outcome. What will pupils produce at the end of the lesson or sequence of lessons that will demonstrate the learning that has taken place – for example, a piece of writing, an artefact, a presentation or the solution to a problem? You will need to be clear from the outset what a good-quality product will look like. This will help you to clarify your expectations with pupils. fall into a number of categories.
The nature of the learning objective – for example, skill acquisition or developing understanding – will determine the approaches and strategies you use.
- This resource is part of the DfES resource "Pedagogy and practice: Teaching and learning in secondary schools" (ref: 0423-2004G) which can be downloaded from the National Archives http://webarchive.nationalarchives.gov.uk/20110809101133/nsonline.org.uk/node/97131 The whole resource (512 pages) can be downloaded as a pdf File:Pedagogy and Practice DfES.pdf
- The resource booklets, and many 'harvested' documents are available to download, generally in editable formats from the ORBIT resources, see Category:DfE.
- The videos from the accompanying DVDs are available: Video/Pedpack1 and Video/Pedpack2