Resources: KS4
- [[Topics/Algebra|Algebra]]
- [[Topics/Area|Area]]
- [[Topics/Astronomy|Astronomy]]
- [[Topics/Geology|Geology]]
- [[Topics/Solar system|Solar system]]
- [[Topics/History|History]]
- [[Topics/Astronomy|Astronomy]]
- [[Topics/Blogs|Blogs]]
- [[Topics/Blogs|Blogs]]
- [[Topics/E-skills|E-skills]]
- [[Topics/Copyright|Copyright]]
- [[Topics/Consecutive Sums|Consecutive Sums]]
- [[Topics/E-skills|E-skills]]
- [[Topics/E-safety|E-safety]]
- [[Topics/Sharing practice|Sharing practice]]
- [[Topics/Curriculum development|Curriculum development]]
- [[Topics/Virtual Learning Environment|Virtual Learning Environment]]
- [[Topics/E-skills|E-skills]]
- [[Topics/Wikis|Wikis]]
- [[Topics/ICT|ICT]]
- [[Topics/Multimedia|Multimedia]]
- [[Topics/Games|Games]]
- [[Topics/ICT|ICT]]
- [[Topics/Investigation|Investigation]]
- [[Topics/Multimedia|Multimedia]]
- [[Topics/Probability|Probability]]
- [[Topics/Scientific literacy|Scientific literacy]]
- [[Topics/Science citizenship|Science citizenship]]
- [[Topics/Reading skills|Reading skills]]
- [[Topics/Study skills|Study skills]]
- [[Topics/Sampling|Sampling]]
- [[Topics/Simultaneous Equations|Simultaneous Equations]]
- [[Topics/Standard Index Form|Standard Index Form]]
- [[Topics/Statistics|Statistics]]
- [[Topics/Wikis|Wikis]]
- [[Topics/Wikis|Wikis]]
Relevant resources
| Area | Circles, frustums and cylinders revision | |

|
Measure the volumes of objects This resource offer students the opportunity to engage in active learning(ta) - measuring and calculating using large size cylinders and frustums. This lesson brings great opportunity for small group "dialogic teaching(ta)". Open-ended and closed questioning(ta) of students can be used to draw on their existing knowledge and extend their understanding. The teacher provides a practical commentary below.
| |
| Astronomy | Celestial Wanderers | |

|
Why would we fly to another planet to study its rocks? Drawing on a rich range of sources, this presentation allows the teacher to introduce planetary geology(topic), something not normally studied until degree level. It uses the narrative(ta) of the Voyager Probes journey to illustrate the vastness of the solar system(topic) and also the challenges of designing a spacecraft to travel that far. It ends with a discussion of the history(topic) of Mars, and how the differences between it and the Earth resulted in Mars loosing its water and atmosphere whereas we have kept ours.
| |
| Astronomy | Astronomy Master Class | |

|
An overview of of six astronomy-related lessons resources (SC019 to SC0024) The Astronomy Master Class was developed to inspire the next generation of scientists and in particular physicists. Although this course of 6 lessons is framed mostly around the science of astronomy, it draws on many themes from physics and aims to show how they all can link together. Additionally, it is structured so that it deliberately does not cut across material in most standard GCSE science courses and does not aim to answer every question. A deliberate part of the design was to visit each topic area only briefly and leave students hungry for more.
| |
| Astronomy | Alien Life | |

|
Are we alone? This last of six presentations to recruit students for A level physics, is more light-hearted and simpler than the two previous resources. It considers the arguments around whether or not humanity is alone and includes an initial look at the bizarre nature of many of the claims of alien encounters - including a fictional one for good measure - before moving onto the more serious side of alien hunting. It concludes with a probabilistic argument based on the Fermi paradox.
| |
| Blogs | Getting a buzz out of blogging | |

|
||
| Consecutive Sums | Using Prime and Square Numbers - How Old Am I? | |

|
Last year I was square, but this year I am in my prime. How old am I? This short activity offers opportunity for pupils to engage in mathematical thinking(ta) and higher order(ta) problem solving/reasoning(ta). They should be able to make links between different areas of mathematics and explore their ideas in whole class(ta) discussion(ta) and questioning(ta).
| |
| Games | Introduction to games | |

|
||
| ICT | Data Logging and Control | |

|
A compendium with numerous ideas for using sensors to teach science. This book provides a set of resources and lesson ideas with ICT(i) as a key focus for use in inquiry(ta) based learning and the scientific method(ta). It offers opportunities for use of group work(ta) and collaboration(ta) as well as whole class(ta) questioning(ta).
| |
| Investigation | Consecutive Sums | |

|
Can all numbers be made in this way? For example 9=2+3+4, 11=5+6, 12=3+4+5, 20=2+3+4+5+6 By definition, a problem is something that you do not immediately know how to solve, so learning how to solve something unfamiliar is not straightforward. Tackling an extended problem is difficult.
This lesson gives pupils an opportunity to engage in mathematical thinking(ta) and develop their higher order(ta) thinking skills on a problem that is accessible but which has interest. For example, the problem is presented in diagrammatic and numerical ways. The plan suggests several visualisation(ta) methods to present the same underlying task. It should be useful for teachers to compare these different presentations and either to select the one that they feel will be most useful for their pupils or explore ways for the pupils to see the links between the different methods. The assessment(ta) ideas, using other pupils' solutions from the NRICH website are widely applicable to other problems too. | |
| Multimedia | Working with multimedia | |

|
||
| Probability | Playing with Probability - Efron's Dice | |
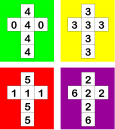
|
I have some dice that are coloured green, yellow, red and purple... Efron's dice provide a discussion(ta) topic for joint reasoning(ta) - whole class(ta) or in group work(ta). Pupils can explore aspects of mathematical thinking(ta) particularly with relation to probability.
| |
| Reading skills | Reading and discussing popular science articles | |

|
Read. Get the world's view and see how science works for real The resource relates to the importance of:
It can be delivered through a combination of homework(ta) (perhaps to find an interesting article), group work(ta) to explore various articles (perhaps in a carousel), and/or use of ICT(i) including PowerPoint files to encourage students to present an area they are interested in. | |
| Sampling | Sampling techniques to assess population size | |

|
| |
| Simultaneous Equations | Love Food, Hate Waste - Simultaneous Equations | |

|
Using real world data to explore simultaneous equations Using a source that was not intended by its creators as a mathematical resource, pupils are introduced to informal ways of solving simultaneous equations.
The lesson starts with an intriguing ‘hook’, pupils are able to use reasoning(ta) skills to find an answer to the problem and can then, later, formalise this in an algebraic context, using their informal work to support the transition to mathematical thinking(ta). whole class(ta) work supports this inquiry(ta) into the data provided. Using a resource not targeted at mathematics specifically encourages pupils to think about maths outside of the classroom. | |
| Standard Index Form | An Introduction to the Standard Index Form | |
Working out the rules according to which a calculator displays large numbers The Standard Index Form is a key idea for mathematicians and scientists. The notion that we choose to write numbers in this way requires some explanation. So in this activity, pupils take part in an investigation(ta) on how standard index form works. This is a higher order(ta) problem solving context where students are encouraged to engage in mathematical thinking(ta). They may be involved in whole class(ta) or small group work(ta) discussion(ta), so they have a good opportunity to practice using mathematical language(ta) and questioning(ta).
This means that students do not need to be able to explain their ideas in full: they can use the calculator's feedback to discover whether their ideas are correct or not. This is also an exciting way for pupils to realise an initial idea that fits the data may need to be extended when new data arises. This resource therefore aims to develop investigative skills, as well as introduce pupils to standard index form in a memorable way. The pupils can later use their knowledge of indices in discussion(ta) and group talk(ta) as they explain what is happening. | ||
| Statistics | Cubic Equations and Their Roots | |
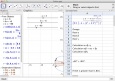
|
To interactiviley explore and understand complex mathematics with GeoGebra This lesson features a ‘real life’ example for students to explore using visualisation(ta) via GeoGebra. The focus on ‘real life’ increases student motivation.
The activity engages pupils in group talk(ta), mathematical thinking(ta) and vocabulary(ta). This open ended(ta) task encourages higher order(ta) thinking, and encourages whole class(ta) discussion(ta)/questioning(ta) and inquiry(ta) projects. | |

